Tips | Script Context in GH Python
Contents
- Script Context
- Spaces to store objects info in GH / Rhino
- Object V.S. Guids
- How to change spaces to work
- Accessing to Rhino Document space
- Create / select objects directly from GH Python
- Object attributes
- Dealing with layer
Script Context
Spaces to store objects in GH Python
There are 3 spaces to store objects information:
- GH document
- Rhino document
- memory space on computer
In GH document and Rhino document, objects we can touch are not objects themselves but just interfaces. Namely, objects – actually they are not objects anymore – in these spaces are just IDs that indicates where the objects are stored in memory space on computer. GH Python can access these objects via rhinoscriptsyntax or ghpythonlibs. In these spaces object attributes, which are like color, layer, material, etc, is stored separately, because objects in these spaces cannot have object attributes.
As for the objects in memory space on computer are able to be dealt with Rhino.Geometry. Objects in memory have object attributes.
Objects V.S. Guids
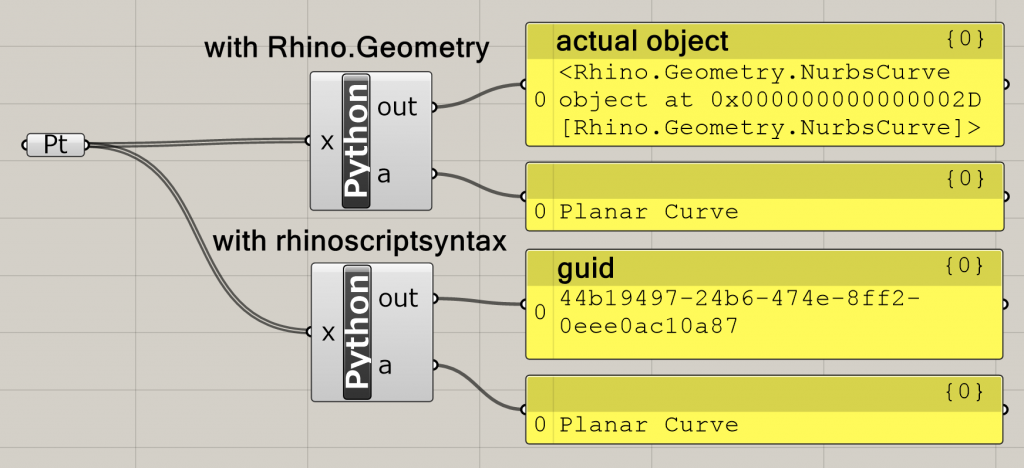
Objects in GH document and Rhino document are called “Guid” and in memory space is called by objects type (Rhino.Geometry…).
Following image is the result displayed on Grasshopper with these 2 codes.
– Rhino.Geometry
import Rhino.Geometry as rg a = rg.NurbsCurve.Create(False,3,x) print a
– rhinoscriptsyntax
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs a = rs.AddCurve(x) print(a)
How to change spaces to work
We can easily change working space between grasshopper document and memory space in computer by changing script libraries. But to change working space into Rhino document, we need to import a function from Rhino. Scriptcontext is the function to change working space between GH document and Rhino document.
To import scriptcontext, you can just type a line at the beginning of your code:
import scriptcontext as sc
and to change space to store objects, you can change doc by making a change in “sc.doc”:
#GH doc to Rhino doc sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc #Rhino doc to GH doc sc.doc = ghdoc
Accessing to Rhino Document space
Now you can access to the rhino document space using scriptcontext. You can easily bake object into Rhino, make some modification in objects in Rhino space, and also deal with layer structure.
Create objects in Rhino directly from GH Python
To add object into Rhino, you can just go to Rhino document with scriptcontext and create object with rhinosctiptsyntax.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs import scriptcontext as sc import Rhino #go rhino sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc rs.AddCurve(x) #back to gh sc.doc = ghdoc
And to move objects from Grasshopper to Rhino, namely to bake objects, you need to format GH objects for Rhino document. And also, you can add some attributes to objects to bake object with certain specifications.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs import scriptcontext as sc import Rhino sc.doc = ghdoc #get object id from grasshopper obj_id = x #convert grasshopper object into rhino object doc_obj = rs.coercerhinoobject(obj_id) #make attributes and geometry from rhino object attributes = doc_obj.Attributes geometry = doc_obj.Geometry #go rhino document sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc #bake object with attributes rhino_obj = sc.doc.Objects.Add(geometry, attributes) rs.ObjectColor(rhino_obj, y) #back to gh sc.doc = ghdoc
Dealing with layer
As you can add objects into Rhino, you can make layers from Grasshopper.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs import Rhino import scriptcontext as sc sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc rs.AddLayer(name="new layer", color=0, visible=True, locked=False, parent=None) sc.doc = ghdoc
But to bake object on certain layer, you need to find layer id on Rhino to identify the layer to bake on.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino
import scriptcontext as sc
#create layer
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
rs.AddLayer(name="new layer", color=0, visible=True, locked=False, parent=None)
#create rhino object
sc.doc = ghdoc
obj_id = x
doc_object = rs.coercerhinoobject(obj_id)
attributes = doc_object.Attributes
geometry = doc_object.Geometry
#select layer to bake and add to the attributes
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
layertable = sc.doc.Layers
layerindex = layertable.Find("new layer",True)
attributes.LayerIndex = layerindex
#bake object
rhino_obj = sc.doc.Objects.Add(geometry, attributes)
sc.doc = ghdoc