Rhino Python Lecture 2016 | DAY2
Contents
- Array(List)
- Functions
- Argument / Return value
- Built-in Functions
- Import Functions(Standard Library)
- RhinoScriptSyntax
- Practice
- Random Points
- Matrix of Points
- Spiral Points Pattern
1. List(Array)
List(Array) is variable that can store multiple values. We can declare array and pick certain value from them like following:
array = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] a = array[4] print(a)
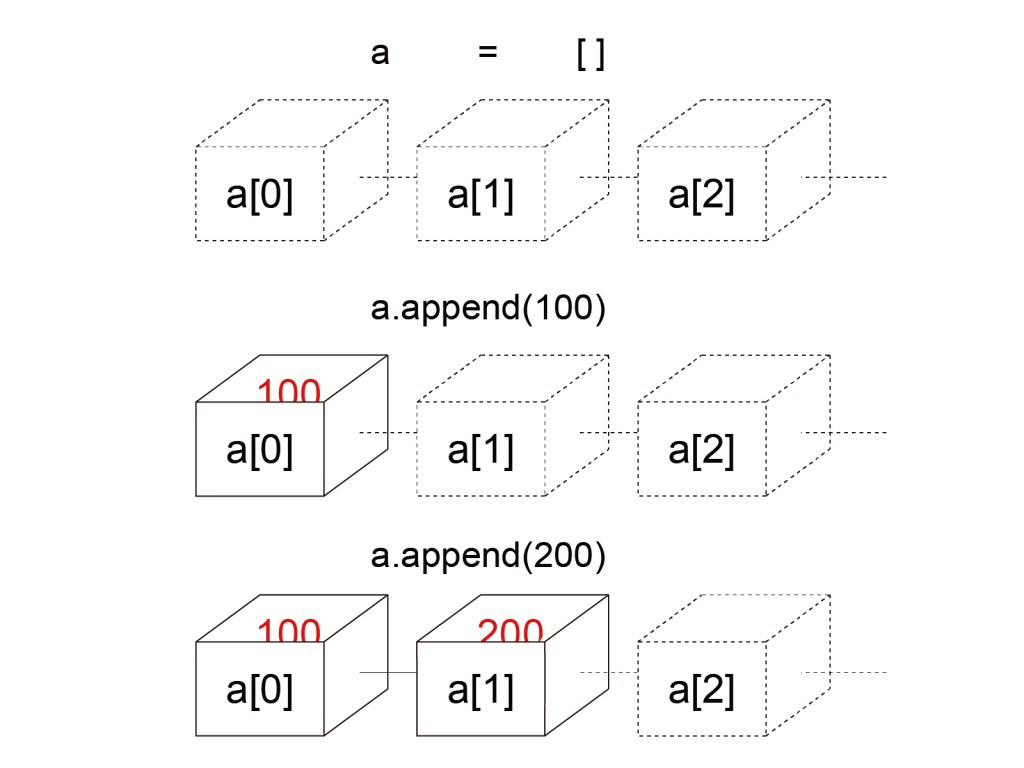
List in python is variable length list and is able to be added or removed .
- .append(val) – add “val” to the last value in the list
- .remove(N) – remove “N”th value in the list
array = [] #blank list
print array
array.append(10)
print array
array.append(0)
print array
array.append('text')
print array
array.remove(0)
print array
For example, the numbers can be stored continuously in combination with For statement
array = []
for i in range(10):
array.append(i)
print array
2. Functions
2.1. Argument / Return value
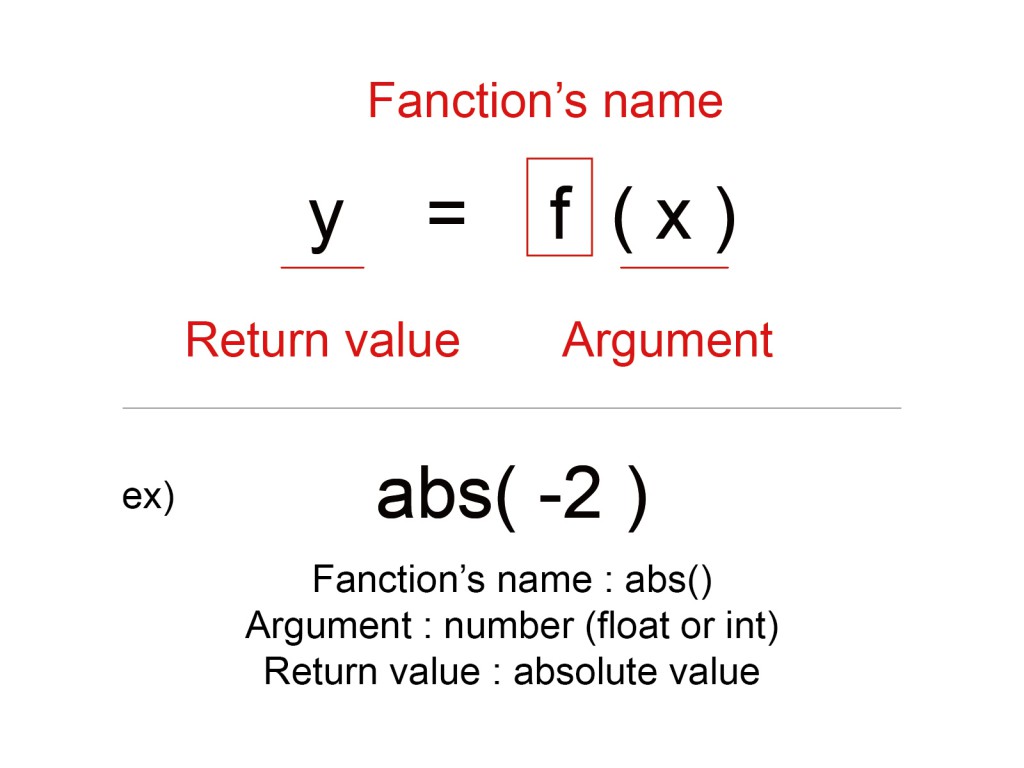
Functions are mathematical formula that have input value(=Argument) and output value(=Return value).
print() is also one of the many python’s functions (but don’t have Return value).
2.2. Built-in Functions
The Python interpreter has a number of functions built into it that are always available.
#############################################################
#Built-in Functions
#############################################################
#abs(x)
#Return the absolute value of a number.
a = abs(-2)
print a
#int(x)
#Return an integer object constructed from a number or string x,
i1 = int(1.2030830)
i2 = int("100")
print i1
print i2
#round(number[, ndigits])
#Return the floating point value number rounded to "ndigits" digits after the decimal point.
#If ndigits is omitted, it returns the nearest integer to its input.
r1 = round(1.913907)
r2 = round(1.913907, 3)
print r1
print r2
2.3. Import Functions(Standard Library)
You can use any Python source file as a module by executing an import statement.
############################################################# #Random Library #Generate random numbers ############################################################# #import random library import random #random.randint(a, b) #Return a random integer N such that a <= N <= b. Alias for randrange(a, b+1). r = random.randint(0, 10) print r #random.uniform(a, b) #Return a random floating point number N such that a <= N <= b for a <= b and b <= N <= a for b < a. u = random.uniform(0.0,10.0) print u ############################################################# #Math Library #Mathematical functions ############################################################# #import math library import math #math.sqrt(x) #Return the square root of x. s = math.sqrt(9) print s #math.pi #It don't have "argument" value. #pi - Ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter; Pi #The mathematical constant pi = 3.141592..., to available precision. p = math.pi print p #math.e #It don't have "argument" value. #e - Napier's constant of natural logarithm #The mathematical constant e = 2.718281..., to available precision. e = math.e print e #math.sin(x) #Return the sine of x radians. s = math.sin(math.pi/4) #sin(45degrees) print s #math.cos(x) #Return the cosine of x radians. c = math.cos(math.pi/4) #cos(45degrees) print c #math.tan(x) #Return the tangent of x radians. t = math.tan(math.pi/4) #tan(45degrees) print t
For more information, you can check — https://docs.python.org/2.7/library/index.html
*
[Tips] – import “as”
############################################################# #Tips #import "as" - Abbreviation definition of library name ############################################################# #import and omit math library to m import math as m #import and omit random library to t import random as r r.uniform(0,10) #it can run. print r m.sqrt(9) #it can run. print m
3. RhinoScriptSyntax
3.1. Import RhinoScriptSyntax
To use Rhino function in python, you can use rhinoscriptsyntax. Using rhinoscriptsyntax, you need to import the library. You can import the library by following:
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
There are bunch of functions in rhinosctiptsyntax. Followings are examples of them.
You can draw a point, circle and polyline like following
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs #rs.AddPoint(x, y, z) #draw a point with x,y,z coordinates obj1 = rs.AddPoint(0,0,0) #rs.AddCircle(center point, radius) #draw a circle with center point and radius obj2 = rs.AddCircle([0,0,0], 100) #rs.AddPolyline(list of points) #draw a polyline with a list of points obj3 = rs.AddPolyline([[0,0,0],[100,100,0],[200,0,0]])
You can move and copy object like following:
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs obj = rs.AddPoint(0,0,0) #rs.MoveObject(object_id, translation_vector) rs.MoveObject(obj, [100,0,0]) #rs.CopyObject(object_id, copy_vector) rs.CopyObject(obj, [0,100,0])
You can get object from Rhino like following:
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs #rs.GetObject() - don't need argument obj = rs.GetObject() rs.CopyObject(obj, [0,100,0])
For more information, you can check at the menu bar of RhinoPython Script Editor
Help -> Pyhton Help
Or check — http://developer.rhino3d.com/api/RhinoScriptSyntax/win/
4. Practice
Please send your program data to Shuta by the end of the day
→ Submission is closed.
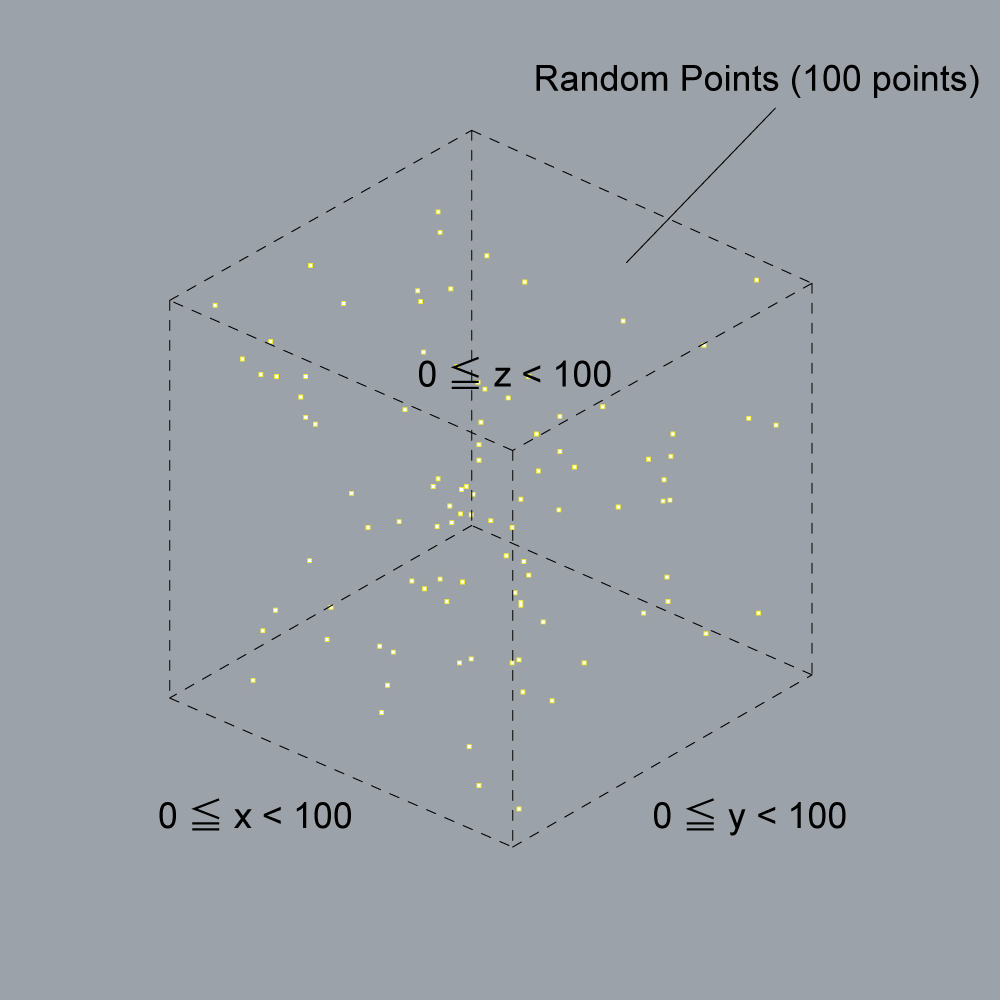
4.1. Random Points
Please plot points as folowing figure by python scripting
4.2. Matrix of Points
Please plot points as folowing figure by python scripting

4.3. Spiral Points Pattern
Please plot points as folowing figure by python scripting
[reference]Trigonometric functions:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trigonometric_functions